What Are The Effectors Of The Nervous System
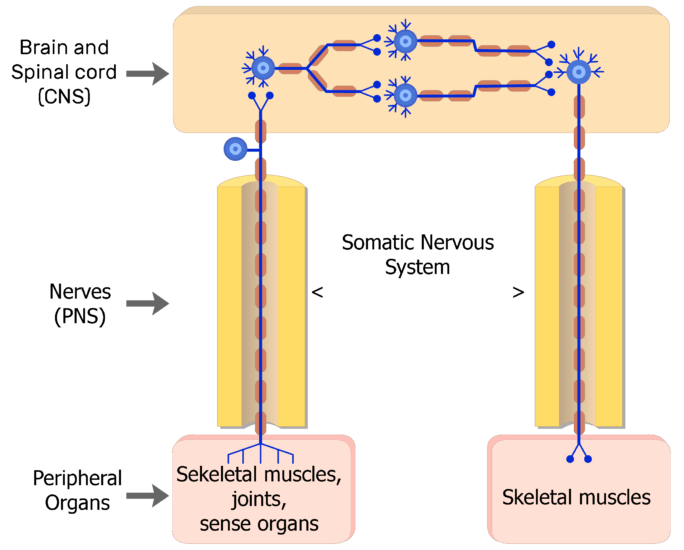
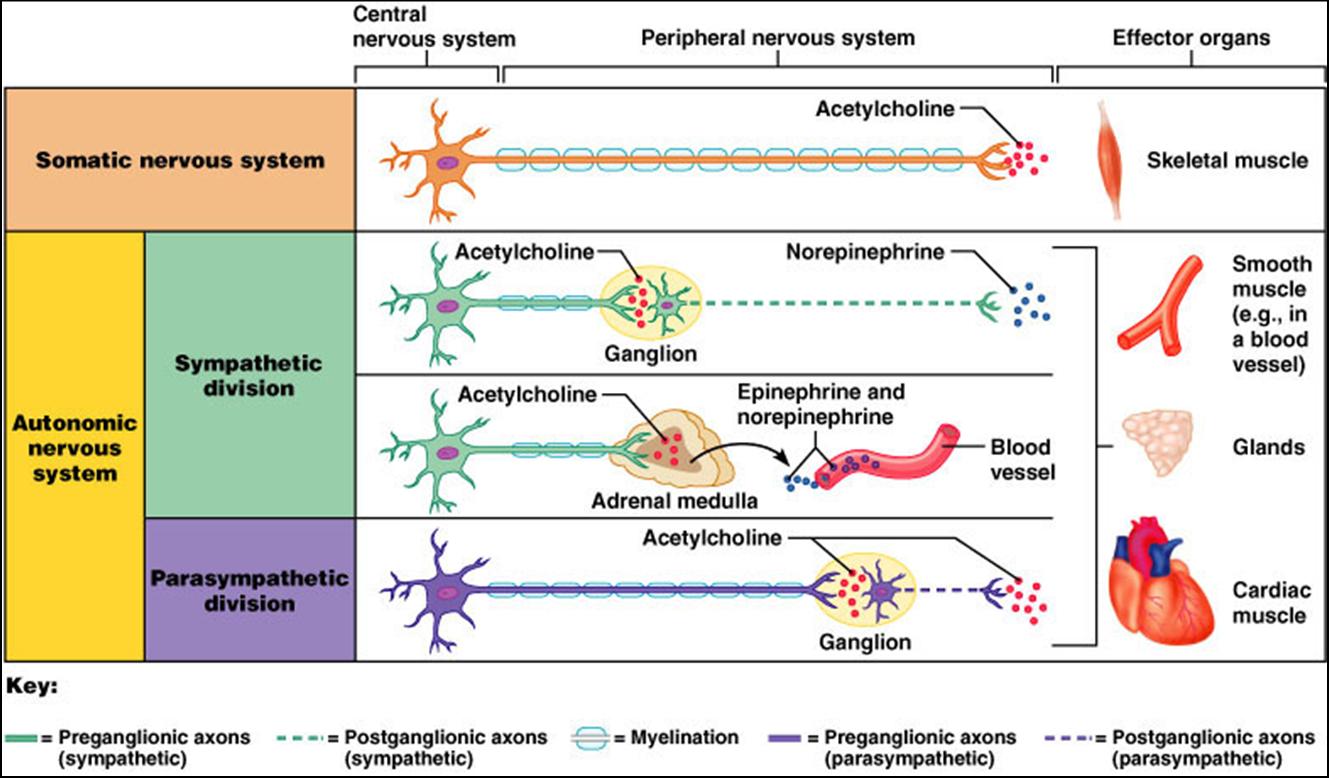
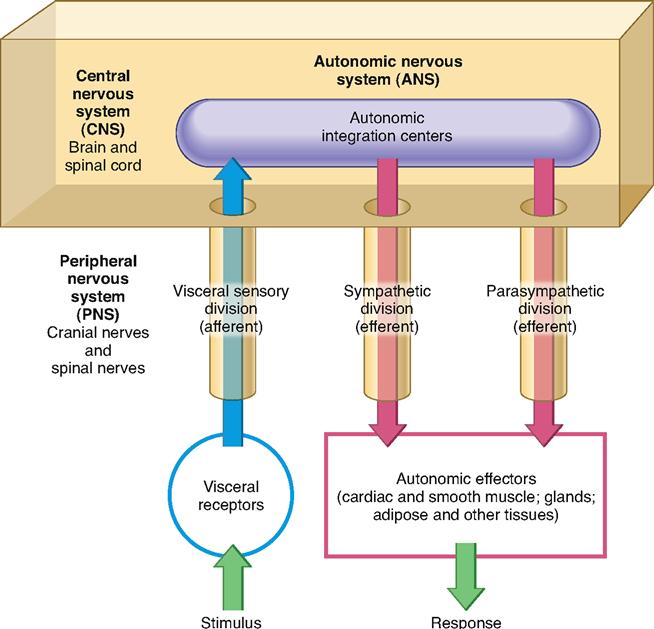
What are the effectors of the nervous system. There are two types of effectors the muscles also called motor effectors and exocrine glands also called secretory efectors. A receptor is the structure that monitors internal conditions. The somatic motor system relays instructions to muscles more quickly because it involves only one motor neuron whereas the ANS uses a two-neuron chain.
All effectors are stimulated by. When these signals reach the end of a neuron they stimulate the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters. Visceral reflexes are reflexes that occur in the soft tissue organs of the body such as the digestive and reproductive system.
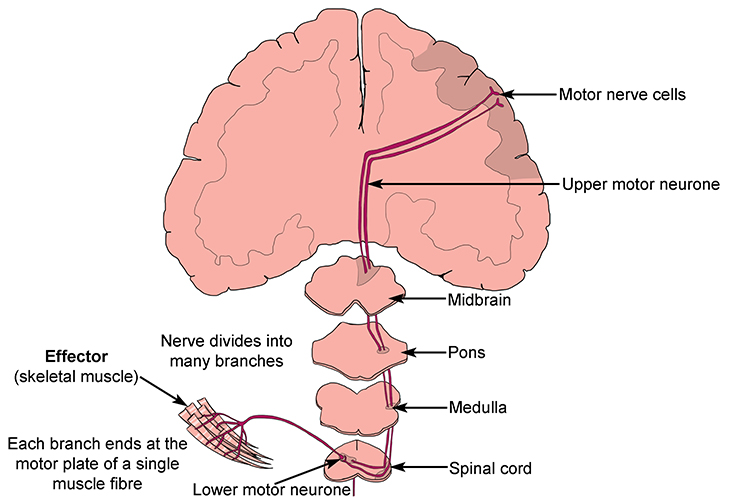
Somatic Nervous System. Muscle squeezing saliva from the salivary. A muscle contracting to move an arm.
The effectors of the somatic nervous system are the skeletal muscles. There are two types of effectors the muscles also called motor effectors and exocrine glands also called secretory efectors. The effectors of the ANS are cardiac muscle smooth muscle and glands What are the efferent pathways of the somatic nervous system.
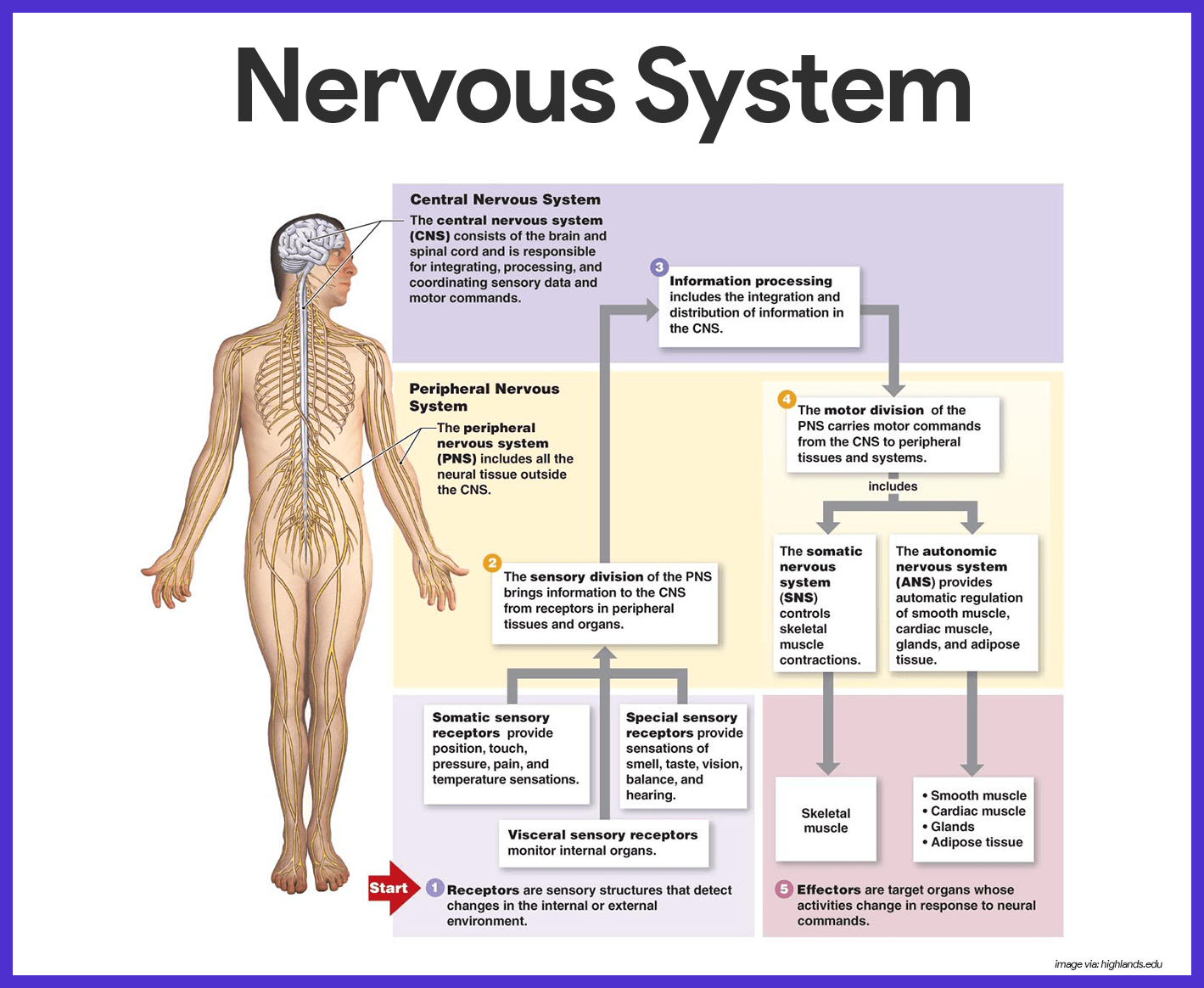
What are the two types of effectors in the nervous system. What are receptors in Homeostasis. The efferent neurons also known as motor neurons of the somatic nervous system.
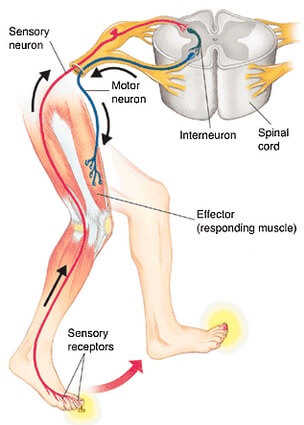
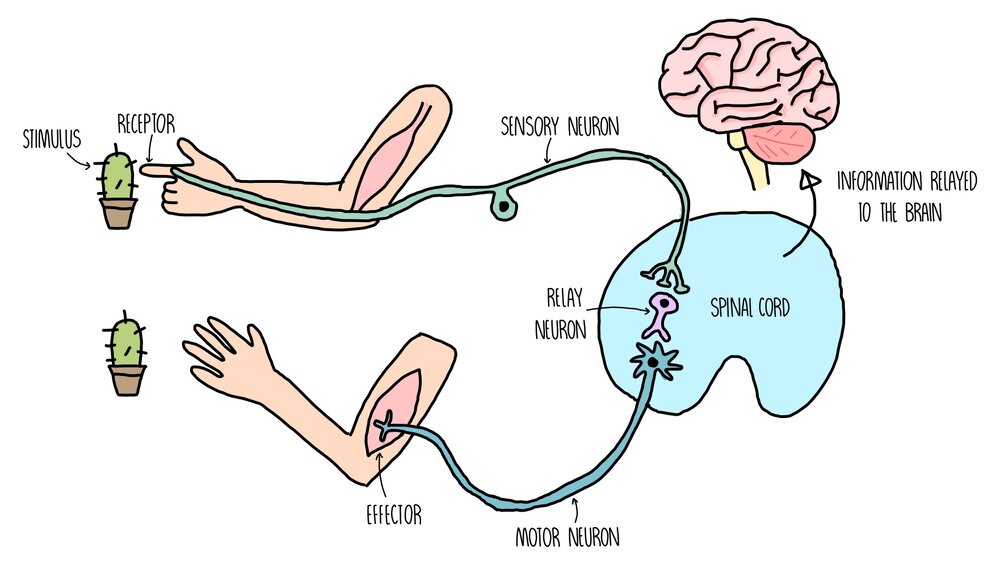
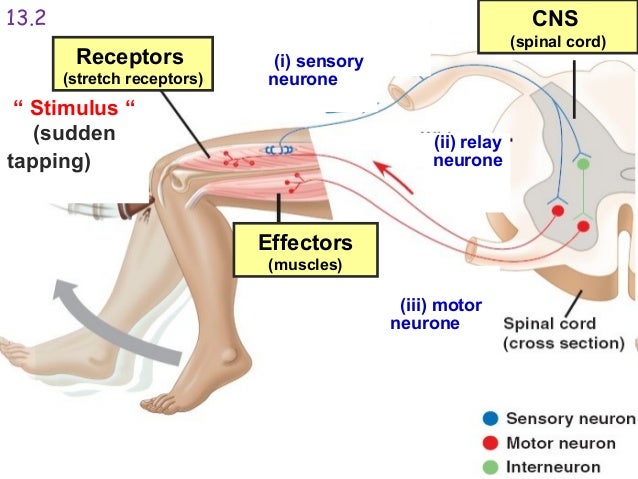
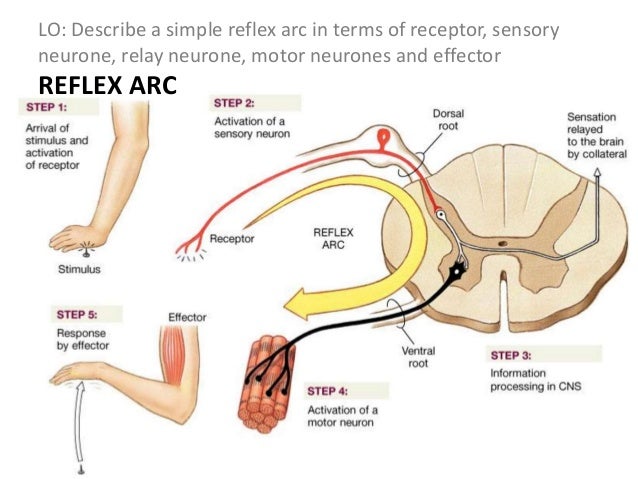
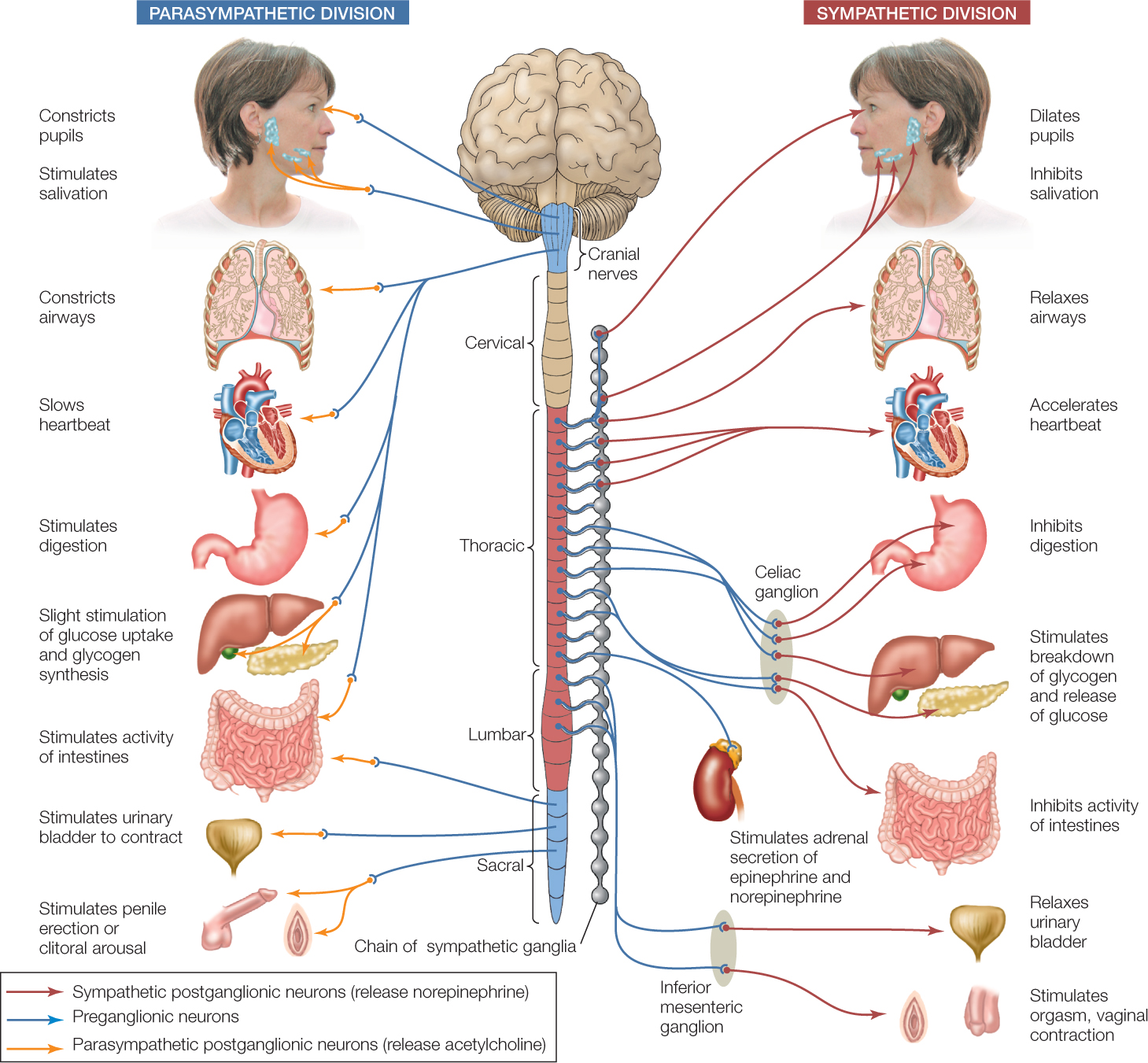
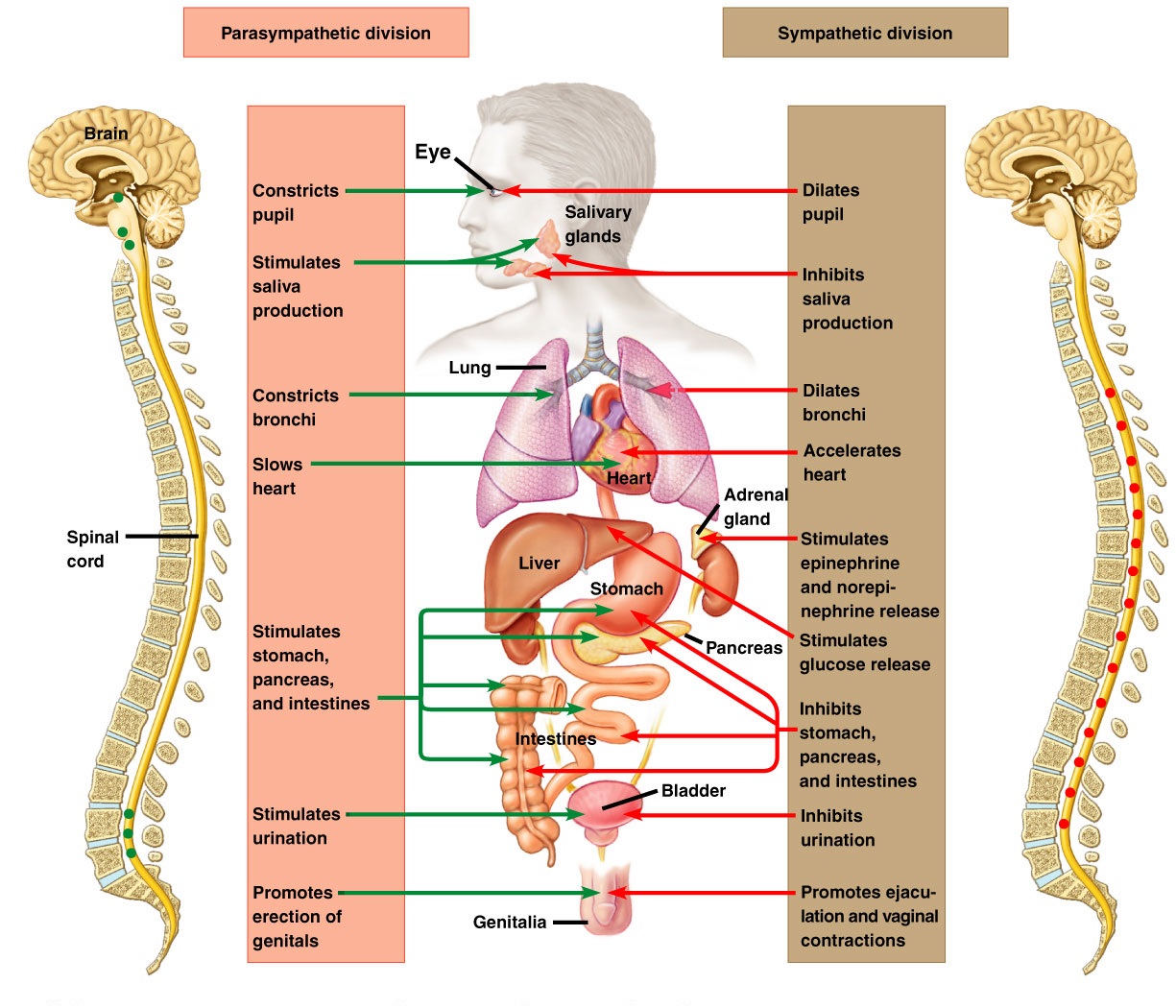
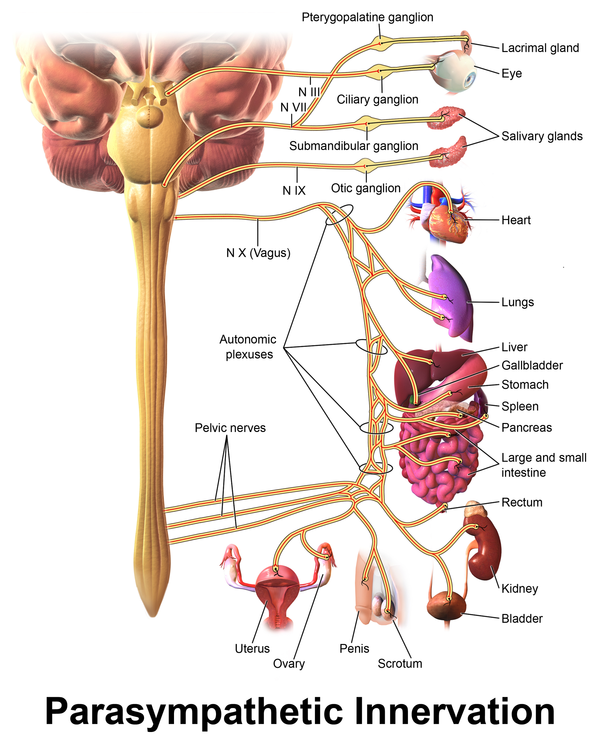
Are the organs that perform the responses of the Nervous System. B the visceral motor division ANS carries signals to glands skeletal muscle and smooth muscle. Effectors include muscles and glands and so responses can include muscle contractions or hormone release.
The effectors of the autonomic nervous system are cardiac muscle smooth muscle and glands. The somatic nervous system always causes the excitatory response at the effector.
Effectors include muscles and glands - that produce a specific response to a detected stimulus.
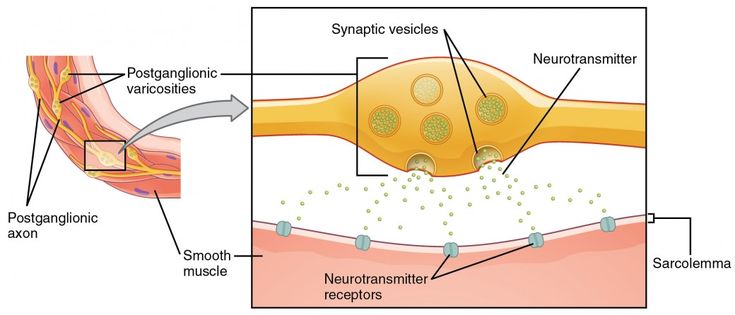
The somatic motor system relays instructions to muscles more quickly because it involves only one motor neuron whereas the ANS uses a two-neuron chain. The autonomic nervous system may cause either excitatory or inhibitory response at the effector. An effector acts in special ways in response to a nerve impulse. What are the effectors of the somatic nervous system. It basically undoes the work of sympathetic division after a stressful situation. An effector is a muscle or gland that receives the impulse from the motor neuron. Nervous system messages travel through neurons as electrical signals. The somatic nervous system releases acetylcholine at the effector. Neurotransmitters travel across synapses spaces between neurons or between neurons and other body tissues and cells.
Effectors are parts of the body - such as muscles and glands - that produce a response to a detected stimulus. An effector is a muscle or gland that receives the impulse from the motor neuron. C the somatic motor division carries signals to the somas of the neurons. Effectors of the autonomic nervous system include smooth muscles of blood vessels cardiac muscle and various glands throughout the body. An effector acts in special ways in response to a nerve impulse. Effectors include muscles and glands and so responses can include muscle contractions or hormone release. Peripheral tissue at the outer end of an efferent neural path one leading away from the central nervous system.























Post a Comment for "What Are The Effectors Of The Nervous System"